Common Dental Problems
Teething
This is the time when baby’s teeth begin to come through the gums. When the teeth break through the surface, the gums may swell and become tender. Teething is easy to spot as your child may become restless or cry frequently. This may also be associated with disrupted sleep and eating habits, low-grade temperatures, cheek redness, drooling and chewing or biting on their toys.
Tips to ease the symptoms of teething.
- Apply ice cubes wrapped in a cold cloth (mindful of ice as a choking hazard).
- Gently massage the gums with your finger.
- Safe teething rings can be used. Watch out for teething rings with liquid inside as the liquid may not be suitable for ingestion in case of rupturing the ring.
- The effect of teething gel is likely to be limited as it will be washed away quickly due to baby's drooling. Applying teething gels before feeding may be effective in pain relief.
- Consider using analgesiscs such as Pamol and follow consumer instructions.
- If there is excessive bleeding, pain, pus or swelling, call Healthline or see your GP.
Teething does not cause serious health problems. High fever, vomiting, diarrhoea, and ear infection are not symptoms of teething. If your child has these symptoms, please contact Healthline or your GP promptly for help.

Pacifier or Thumb Sucking
Many parents choose to have their infant suck a pacifier or dummy to calm them. Some children may also suck their thumb or finger. Most children discontinue this habit between the ages of two and four. The effects of these habits on teeth are minor for children under age five, but if used beyond that it may cause problems in the way the permanent teeth develop.
Never dip the pacifier in sugar, honey or other sweetened drinks.
Lift the Lip Screening
Early childhood caries (ECC) is the term used to describe the form of dental caries that affects the teeth of infants and young children. Early identification of this caries can help prevent or stop the progression of this disease.
Parents should lift their child's lip regularly to check for signs of tooth decay.
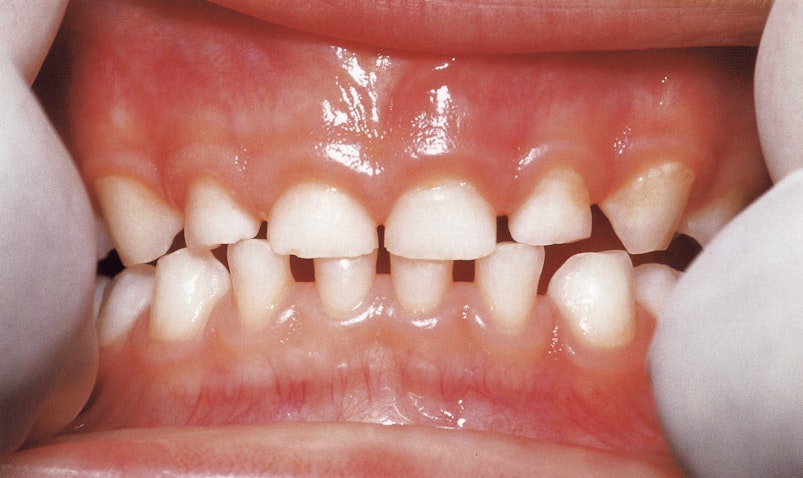
Stage 1: Good
Twice daily brushing with fluoride toothpaste will help keep your child's teeth healthy
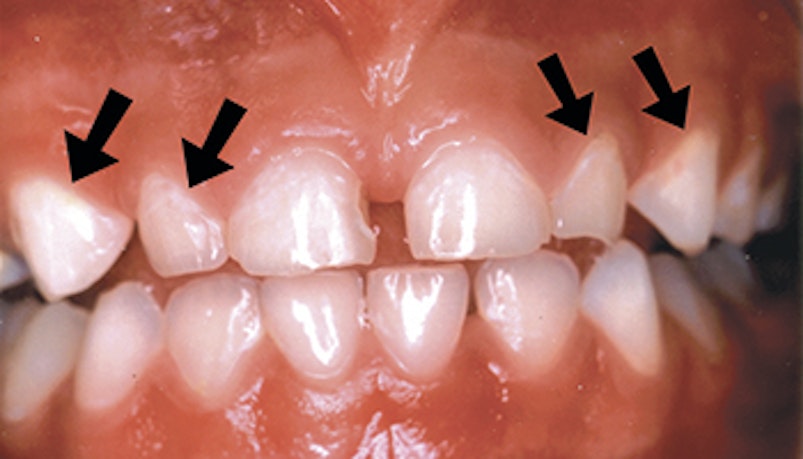
Stage 2: Warning
Chalky, white spots or lines near the gums are signs of early decay. Seek dental care now for advice and treatment to help stop these chalky areas turning into cavities.
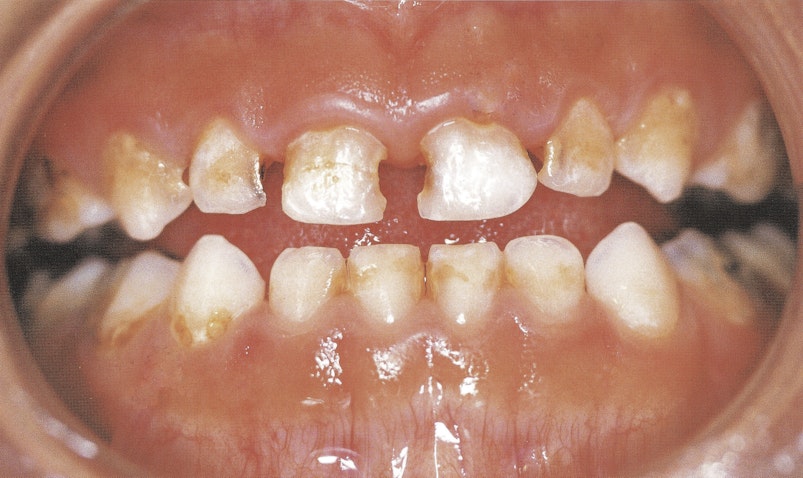
Stage 3: Danger
Brown marks and cavities mean your child needs dental care now to prevent toothache and infections.
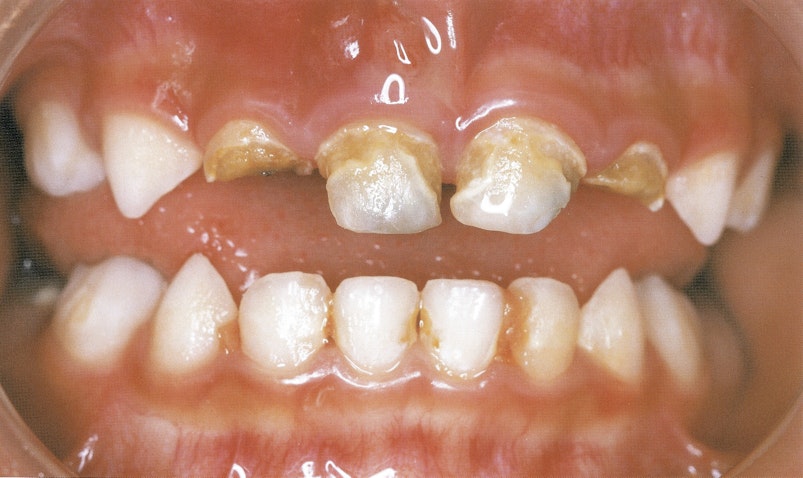
Stage 4: Emergency
Broken teeth and abscesses mean you child will have toothache. They need dental care now to prevent more pain and the infection spreading.
FREE Community Oral Health Service
Oral health treatment is free for 0 – 17-year-olds in New Zealand.
Call 0800 TALK TEETH (0800 825 583) to enrol your child in your regional community oral health service. You can also phone this number to check whether your child is already enrolled or to update your contact details.

